Early Signs And Prevention Of Urogenital Cancer In Men
Malignant neoplasms developing in general urinary tract are commonly referred to as urogenital system cancers. This grouping includes kidney cancers, prostate cancers, bladder cancers and testicular cancers. Although all of these diseases demonstrate certain similarities they are in fact different in terms of their behavior and respond to different treatment, so genital organs cancer as well as urinary tract cancer are just convenient generalizations which include a variety of actual diseases. Therefore, in order to detect and prevent them, every type should be approached separately.
Bladder cancer
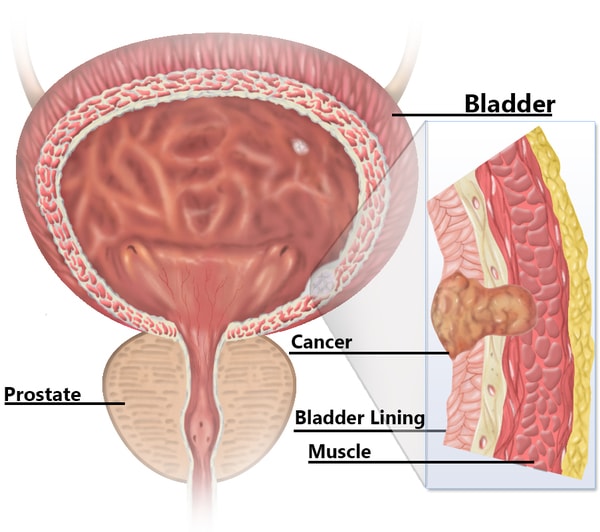 The lining of a bladder consists of transitional epithelium so almost any kind of a neoplasm developing in urinary bladder essentially takes its beginning in the cells of that tissue. Hence the other name – transitional cell carcinoma, although it might refer to a more general case of urinary tract cancer. It is currently estimated to be 5th of the most widespread types of cancers in the US and the most common urinary tract cancer with a preponderance of men over women. Over 68,000 people are affected by the disease which is also associated with more than 14,000 deaths. Men above 50 years are especially susceptible. – the age/occurrence correlation can be explained by continuous exposure to the risk factors (namely, carcinogens). So if you smoke for over 50 years your body will accumulate the damage after fifty years of cigarette smoke.
The lining of a bladder consists of transitional epithelium so almost any kind of a neoplasm developing in urinary bladder essentially takes its beginning in the cells of that tissue. Hence the other name – transitional cell carcinoma, although it might refer to a more general case of urinary tract cancer. It is currently estimated to be 5th of the most widespread types of cancers in the US and the most common urinary tract cancer with a preponderance of men over women. Over 68,000 people are affected by the disease which is also associated with more than 14,000 deaths. Men above 50 years are especially susceptible. – the age/occurrence correlation can be explained by continuous exposure to the risk factors (namely, carcinogens). So if you smoke for over 50 years your body will accumulate the damage after fifty years of cigarette smoke.
Most common risk factors for bladder cancer include:
- Tobacco (3-5x risk compared to non-smokers). – Although it is notorious that smoking is a primary cause of lung cancer but very few know that it’s the same case for bladder cancer (and the correlation coefficient is almost equally significant as for a lung cancer).
- Certain chemicals such as aromatic amines (dyes, rubber, aluminum) – industrial workers working with these substances are more likely to discover a tumor early on.
- Any prior undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy might lead to an increased risk of cancer development (e.g. damaged internal tissues as a result of those exposures may lead to tumor formation).
- It is also worth mentioning that there is a particular type of water-dwelling parasite which is linked to a particular type of bladder cancer. Fortunately, these parasites are mostly found in the Middle East and very rarely – in the US.
- Finally, there is a positive correlation between recurrent urinary tract infections and cancer.
Stages
Interpreting correctly early signs of disease or urogenital cancer symptoms is crucial for your possible recovery. According to WHO data over 60% of urinary system cancer cases are curable so spreading awareness about the disease progression to make people realize the seriousness of such concerns (esp. if not unfounded). Moreover, some symptoms are extremely rare if not unique because of some pre-existing conditions which, combined with tumor development, resulted in some symptoms generally unassociated with cancer at all. Nonetheless, early detection of such anomalies proved beneficial for a patient as medics managed to localize and to contain a would-be lump.
Bladder tumors do not seem to reveal itself during the early stages – at the time the only hint about cancer might be obtained by a direct examination of a bladder from the inside. However, even this doesn’t guarantee the absence of cancer-free life as even spotting some little frond-looking growth in a bladder does not necessarily imply the presence of cancerous cells. But if there is actually a tumor to be concerned about it will eventually grow ripping blood vessels along the way – that results in presence of blood in the urine (more on that in Symptoms subsection).
The stages of bladder cancer development are the following:
- Uncertainty and lack of evidence of tumor
- Formation of a papillary non-invasive tumor
- “Flat tumor” – already formed neoplasm yet still without malignant inclination
- Initial growth phase before reaching muscular wall
- Cancer cells advance into the muscular coat
- Tumor continues its spread to adjacent organs
The first three stages don’t require an oncologist as at these stages a competent urologist is able to manage your treatment at hand and minimize tumor recurrence in the future.
Early signs
Blood in the urine (or hematuria) that doesn’t go away in a day or two is your first red flag to start being concerned – this one of the very common symptoms of urinary tract cancer. But you might not be able to spot blood every time. In a gross hematuria case urine turns almost completely red or pinkish thus it is visible to you. But sometimes there are very few blood cells in the urine so it might only be spotted with special tools (microscope or chemical analysis). Still, blood presence doesn’t necessarily indicate its cancerous cause – any kind of foreign agents in your body might’ve caused blood – viruses, bacteria, benign tumors, kidney/bladder stones. This internal bleeding is possibly accompanied by pains during urinating and doing the latter frequently maybe even with difficulty alongside with burning sensation.
If for whatever reasons you ignored the symptoms described above the odds are you’ll experience some other symptoms.
In rare cases, their appearance coincides with first blood in the urine appearance.
- Inability of urinating
- Pain on one lower side of the back
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Bone pain
Aforementioned symptoms are not limited only to bladder cancer and it’s impossible to tell whether you have bladder cancer or urinary tract infection. So be sure to consult your urologist before undergoing any kind of treatment.
Preventive measures
There are not so many ways to prevent bladder cancer and most of them derive from the risk factors.
- Don’t smoke. One scientist said once during a public lecture that if everybody had quit smoking immediately bladder cancer occurrence would’ve dropped 60-70%. Whatever your other exposures are, tobacco simply doubles the odds of a tumor appearance.
- Go through the risk factors again – if there are some of them that affect you on a regular basis be sure to avoid or at least minimize your exposure to these factors.
- Drinking a lot of liquids is a helpful practice – the reason is that the more liquid goes through your body the less is a period of continuous exposure of your bladder tissue to carcinogens.
- A healthy diet with a lot of fruits and vegetables – there is some evidence backing a theory that when tissues have sufficient amount of vitamins available they are more resilient to cancerous effects.
Testicular cancer
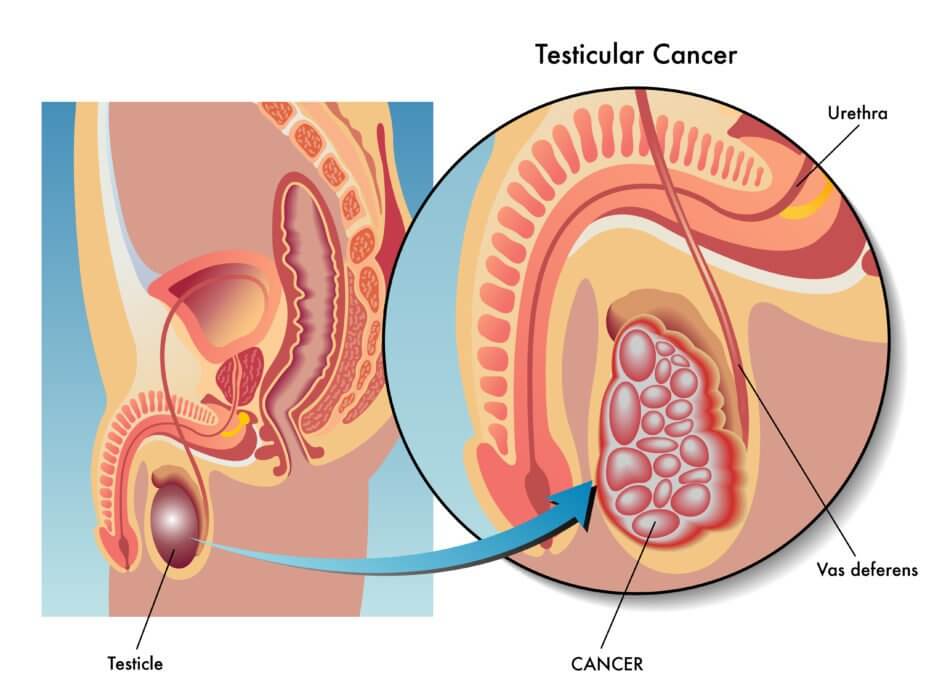 In order to understand the causes of cancer occurrence in testis, you should be aware of some complex biological mechanisms involved in sperm and testosterone production. Primarily whenever cancer spreads it usually is confined to germ cells present in a body – these cells are responsible for sperm production. Other cases might involve Sertoli/Leydig cells malfunction – that results in excessive amounts of either testosterone or estrogen being present in your blood. These cases manifest themselves by enhanced masculine features (e.g. a redundant muscle bulk) or feminine features (e.g. large breasts). In the US there are 8,000 new cases of testis cancer diagnosed and it causes over 500 deaths yearly – that makes it 10th most common cancer in the US. Occurrence-to-deaths ratio is relieving in a way that, for example, for pancreas cancer, it equals somewhere around 0,95-1 meaning that every new case is almost inevitable death. However, for young men aged 15-35, this is the most common cancer. But again, even testicular cancer with distant metastases present is highly curable – one of the most widely known examples in Lance Armstrong who sought medical help when the disease spread to his abdomen, lungs, and brain. The treatment received by Mr. Armstrong was a combination of surgery and chemotherapy yet he was able to fully recover and get back to serious training for racing in two years.
In order to understand the causes of cancer occurrence in testis, you should be aware of some complex biological mechanisms involved in sperm and testosterone production. Primarily whenever cancer spreads it usually is confined to germ cells present in a body – these cells are responsible for sperm production. Other cases might involve Sertoli/Leydig cells malfunction – that results in excessive amounts of either testosterone or estrogen being present in your blood. These cases manifest themselves by enhanced masculine features (e.g. a redundant muscle bulk) or feminine features (e.g. large breasts). In the US there are 8,000 new cases of testis cancer diagnosed and it causes over 500 deaths yearly – that makes it 10th most common cancer in the US. Occurrence-to-deaths ratio is relieving in a way that, for example, for pancreas cancer, it equals somewhere around 0,95-1 meaning that every new case is almost inevitable death. However, for young men aged 15-35, this is the most common cancer. But again, even testicular cancer with distant metastases present is highly curable – one of the most widely known examples in Lance Armstrong who sought medical help when the disease spread to his abdomen, lungs, and brain. The treatment received by Mr. Armstrong was a combination of surgery and chemotherapy yet he was able to fully recover and get back to serious training for racing in two years.
Risk factors
There was a fair amount of research looking at why do men develop testis cancer and the general conclusion to this question would be 3 outlined risk factors:
- Undescended testis – means failure of testicle descent into the scrotum during mid-late pregnancy period. A common explanation is that this is the result of some abnormalities of testicle development along with inborn genetic instability. It isn’t usually revealed right away thus the abnormality progresses leading to cancer.
- Family history – if a father or brother has testis cancer you are more likely to develop it
- Prior history of testis – for men who already suffered from testis cancer there is 8% lifetime contralateral risk (i.e. the risk of cancer occurrence on the other side). What it means is that there is some genetic basis formed by a prior tumor, so a male is more predisposed to develop it again.
Early Signs
Admittedly, there are probably more factors which are still not recognized to this day. Still all types of testicle cancer (except some extremely rare cases) share common symptoms by which you might be able to recognize tumor early.
These are:
- Generally painless testis mass – the skin covering a scrotum is relatively thin thus making tumor detection very easy by simply palpating the area.
- Rare symptoms include back pain and back part of the belly which is linked to tumor spreading across adjacent body parts. Rare symptoms derive from a particular stage testicular cancer is at, so when it is confined only to testicles – that’s stage 1 and it is identifiable only your own self-examination. Stage 2 (retroperitoneum) is directly connected with aforementioned back pains and stage 3 defines a situation when cancerous cell are present somewhere above the diaphragm or in other organs, so there are some possible rare symptoms but by that time most of the diseased males find their way to the doctor.
Prevention
The question of prevention testicles cancer has no definite answer. The main challenge remains genetic nature of most of the risk factors and as a consequence your inability of to influence these factors. But having a habit of examining your scrotum after a warm shower might be helpful as your skin will get smoother making detection of any neoplasm easier. So the recipe here is to simply palpate the area where your testicles are located. As you get used to knowing your normal condition it will be much easier for you to detect even a small lump (usually painless) and get a timely medical treatment.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a malign neoplasm that forms in the tissues of the prostate gland. The latter is located at the base of the bladder and this is where in 90% of all cases the disease is located when diagnosed. However, 1 out of 7 men is diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime and 1 out of 50 people dies from it. This particular type cancer has higher mortality ratio than any other urogenital system cancer.
Risk factors:
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer:
- Men of older age – the incident rates are increasing exponentially with age. It should be mentioned that across all ages African-Americans have much higher risk of prostate cancer development than Caucasians, Hispanics, and Asians.
- Consuming processed meat (esp. processed red meats) intake has to do with carcinogens that are created when you cook or process meat at high temperatures. It is also important to distinguish risks of developing PC and risks of its progression as a recommended diet for a patient already diagnosed with PC might exclude meals such as cooked tomato products or fish.
- Foods high on calcium (Dairy, Milk) have been consistently associated with a moderate elevation in risk. This happens in part because high intakes of calcium tend to suppress endogenous production of active metabolite of vitamin D and the latter is argued to be able to deter tumor progression
- Smoking – again. In spite of general perception of smoking as a main contributor to the lung cancer, it’s also true for prostate cancer (as for any other male urogenital cancer).
Early signs:
One of the main problems associated with prostate cancer is an absence of any symptoms for you to recognize. Partial changes in voiding patterns are generally disregarded at early stages. Moreover, any other symptom, although known to occur during prostate cancer progression might as well indicate many other diseases – blood in urine, pain when ejaculating, frequent urination – none of them are PC-specific and without running special tests urinary tract infection and prostate cancer are perfectly indistinguishable. There are a lot of tests which might be conducted by a physician, yet again indicators such as high PSA level are inaccurate at the earliest cancer stages and methods like digital rectal examination aren’t suited for detecting small lumps.
Prevention:
It was proved that men with a close relative who suffers or suffered prostate cancer are more susceptible to the disease. However, being born of a particular race or to age aren’t exactly things we can have any influence on. So although these are undoubtedly risk factors, they are unmodifiable. But there are factors you can affect directly thus reducing the risk and prevent prostate cancer.
- Diet
Limit your daily fat intake – consume less of aforementioned products such as milk and dairy products along with different kinds of oils and meats.
Foods rich in lycopene such as tomatoes and tomato pastes are natural antioxidants which are helpful in several types of cancer (prostate cancer included). Make sure these are present in your diet. There is also some evidence that these products prevent the development of urinary tract infection after prostate cancer.
Foods rich in selenium are crucial for your body to process fats – products like brazil nuts or canned sardines will be beneficial for your diet. Also, consider taking selenium supplements only after consulting with your doctor.
- Body size, Exercise – maintain a healthy weight – either by limiting your calories intake or exercising more or both.
Kidney cancer
In order to perform its functions properly (filtering blood that is) kidneys are stocked up with many types of tissue – exactly the reason why there are different kinds of neoplasms with malignant potential possibly occurring. However, 90-95 per cent of people suffering from kidney cancer is diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma. It also composes 63% of all cases of urinary tract cancer in males. That is why the information presented here will primarily cover this particular kind of cancer. Although not as common as a lung cancer, statistically those suffering from renal cell carcinoma have are more likely to discover a significant spread of the disease at a time of diagnosis (with over 20 per cent of all RCC cases metastasized in other parts of the body).
Risk factors:
- Smoking – as with any other type of urinary tract cancer, harmful chemical intake from smoking doubles the risk of cancer occurrence.
- Hypertension
- Obesity
- Chronic kidney diseases
- Exposure to toxins
- Misuse of analgesics (acetaminophen, aspirin, NSAID) and similar pain meds
- Sickle cell disease (renal medullary cancers)
- Hereditary diseases
- Family history of RCC
Early Signs:
Certain challenges are linked to diagnosing renal cell cancer as a patient himself might not experience any symptoms.
- Weariness and Fatigue – if experienced for an unusually long period of time it may be an indicator of RCC. Because of the lowered blood cell count or anemia, you’re unable to fully regain your strength. However, the opposite is also possible – a tumor is capable of producing erythropoietin which causes a surge in red blood cell count (erythrocytosis)
- Back pains – as a lump continues growing it will start pressing against adjacent organs and surrounding tissues. The problem is that because of a deep displacement of kidneys you’ll be able to feel the pain only in case of tumor advancement.
- A palpable lump mass on your back or side – usually appears after continuous ignoring of back pains.
- Hypocalcemia – genetic alterations in tumor cell affects many aspects of a renal cell. Either because of production of a particular protein or via shifts in complex hormone machinery the result stays the same – a continuous release of calcium in your blood.
- Neoplastic fever – short-term fevers that happen in absence of any progressing infection
- Loss of appetite and consequential weight loss
- Leg swelling – the veins that drain the legs are obstructed by extension of a tumor into a central vein of the body. Scrotal swelling is also possible for the very same reasons.
Prevention:
Kidneys are naturally more susceptible to any toxic substances inhaled or ingested into your body as they filter out and temporarily store these substances before egesting. That’s why it is important to reduce your intake of toxins or any other harmful substances. Tobacco is one of the main sources of harmful chemicals in your body so you should quit smoking. Other preventive measures will be maintaining a healthy weight (thus reducing kidneys’ workload) and keeping your blood pressure in check.